Hello people! In this post, we will talk about a generic tree data structure which is N-ary tree or also known as k-way tree. N-ary tree is defined as a rooted tree which has at most N children for any node. So, a binary tree is a special case of the N-ary tree, where N = 2. Example –
 The above example is a N-ary tree with N = 3. You can observe that each node has no more than 3 children.
The above example is a N-ary tree with N = 3. You can observe that each node has no more than 3 children.
In many scenarios, having a binary tree many not be enough as a situation can often lead to more than 2 situations. In such cases, we must form a N-ary tree of sufficiently large N.
Implementing N-ary tree using structures
Implementing N-ary tree is very simple. It is even more easy if you already know how to implement a Trie Tree. Now, in the case of binary tree, the node structure was like this –
class TreeNode {
String label;
Node leftChild, rightChild;
}
Having two references was enough for us then because we knew we would have at most 2 children. Now, we can have at most N children. How will you store a collection of N references? By using an array! In the case of Java, I’d like to use an ArrayList rather than an array. In the case of C++, I’d suggest you go for a C++ STL vector. So now our node structure will look like this –
class NaryTreeNode {
String label;
ArrayList<NaryTreeNode> children;
int n;
}
Storing the value of N inside the node will enable us to put a restriction on the number of children. So we will add methods inside our newly formed NaryTreeNode class to manipulate the member variables. Some important methods would be –
- addChild(child) – to add a child node.
- getChildren() – to get all the child nodes.
- getChild(index) – to get child at a certain index.
- print(root) – to print the tree. (This can be a static method, where we just supply the root node).
Also, don’t forget to add a constructor to your class! Now you are all set to write the code for N-ary tree. Try to code it, this is something you should be able to code in 1-3 attempts. You can refer to my code below if you get stuck –
Matter
Pure
Elements
Metals
Metalloids
Non-metals
Compounds
Water
Carbon dioxide
Salt
Mixture
Homogeneous
Air
Vinegar
Heterogeneous
Colloids
Suspensions
I have added a helper method for printing the tree so that the tree can be printed more legibly based on the depth of nodes. I have also modified the addChild() method a little. It only accepts the new child’s label as it’s N value can be deduced from the parent node. The code should be easy to understand. Do leave a comment if you have any doubts 🙂
Implementing N-ary tree using arrays
Remember you can implement a binary tree using arrays. Similarly, you can also implement an N-ary tree using arrays. It is very similar to how you would do it in the case of binary trees, so here the formula for computing child node and parent node changes.
Using the above table, you can find the parent and child node for a node at index i. Generally, I like to implement the tree using structures, but if you have a complete n-ary tree, then the array representation will you a better compact storage.
I hope this article was able to give you an idea of how to implement an N-ary tree. Keep practicing! Happy coding! 😀

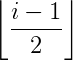
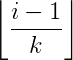
One thought on “N-ary tree or K-way tree data structure”